When it comes to powering your vehicle, boat, or off-grid energy system, the choice of battery is crucial. The two most common types are AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat) and regular (flooded lead-acid) batteries.
Understanding the differences between these battery types can help you make an informed decision. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison of AGM and regular batteries, highlighting their key differences, advantages, and ideal applications.
AGM batteries, known for their maintenance-free nature and resistance to vibration, are often the go-to choice for many. On the other hand, regular batteries, with their lower upfront cost and wide availability, continue to be a popular choice.
Whether you’re an automotive enthusiast, a renewable energy user, or someone interested in reliable battery solutions, this guide will help you understand the pros and cons of AGM vs regular batteries. Let’s delve into the world of batteries and find the best fit for your needs.
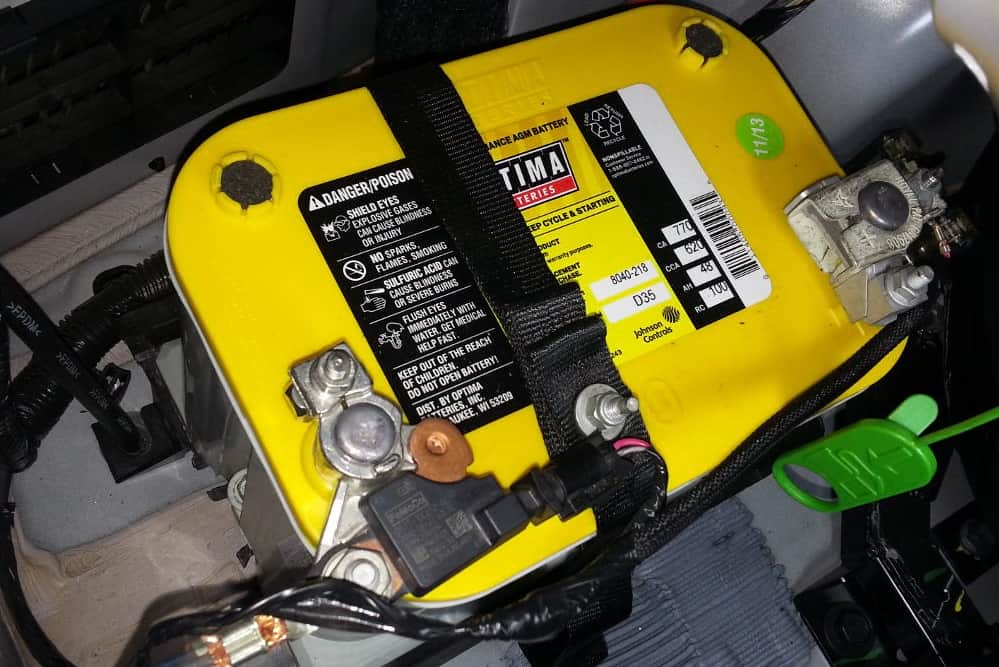

What Are AGM Batteries?
AGM batteries are a type of sealed lead-acid battery known for their innovative technology. The “AGM” stands for Absorbent Glass Mat, which holds the electrolyte. This mat is a crucial component that allows AGM batteries to be leak-proof.
These batteries are renowned for requiring no maintenance. Unlike regular batteries, you won’t need to top them up with water. This feature makes them highly convenient for users who prefer a low-maintenance option.
AGM batteries also excel in areas where vibration and shock resistance are vital. This design aspect makes them particularly suitable for rough environments, such as off-road vehicles or power sports.
Another advantage of AGM batteries is their flexibility in mounting positions. Due to their sealed design, you can mount these batteries in almost any orientation without risking spills.
Here’s a quick summary of AGM battery features:
- Maintenance-free: No need for water replenishment.
- Spill-proof: Safe in various mounting positions.
- Vibration-resistant: Ideal for rugged conditions.
- Fast Charging: More efficient than regular batteries.
- Longer Service Life: Typically outlasts regular options.
These attributes are just a few reasons why AGM batteries are increasingly popular in demanding applications. They provide reliable performance and high energy density, making them a preferred choice in many settings.
What Are Regular (Flooded Lead-Acid) Batteries?
Regular batteries, commonly known as flooded lead-acid batteries, use a liquid electrolyte. This liquid is free to move within the battery case, distinguishing them from their sealed counterparts.
These batteries require periodic maintenance, which often includes topping up with distilled water. This necessity arises because the electrolyte evaporates over time. Therefore, regular monitoring is crucial.
Flooded lead-acid batteries are known for their cost-effectiveness. They often cost less upfront than AGM batteries, making them an attractive choice for budget-conscious consumers. However, their long-term costs may vary due to maintenance needs.
Despite being economically priced, these batteries have drawbacks. They emit hydrogen gas during the charging process. Thus, proper ventilation is essential to prevent dangerous gas buildup.
An important consideration for regular batteries is their sensitivity to charging conditions. They are more forgiving than AGM batteries, but improper maintenance can lead to issues like sulfation. Regular batteries also benefit from periodic equalization charges to prevent battery degradation.
Here’s a summary of regular battery characteristics:
- Requires Maintenance: Needs water refills.
- Cost-Effective: Lower initial investment.
- Produces Hydrogen Gas: Requires ventilation for safety.
- Prone to Sulfation: Needs careful charging management.
- Larger and Heavier: May require robust supports.
These attributes underline why flooded lead-acid batteries remain a popular choice, despite the extra attention they demand. They suit applications where maintenance is manageable, and cost is a key factor.
Comparing AGM and Regular Batteries: Key Differences
AGM and regular batteries vary in many critical aspects. Understanding these can guide you to the right choice.
AGM batteries are sealed, using an absorbent glass mat to contain the electrolyte. This design makes them maintenance-free and spill-proof. Regular batteries, with their free-flowing liquid, often need distilled water top-ups.
The charging process differs notably between the two. AGM batteries charge faster and more efficiently. They have a lower self-discharge rate compared to regular batteries.
Regular batteries, on the other hand, may emit hydrogen gas during charging. Adequate ventilation is essential to ensure safety in enclosed spaces.
AGM batteries handle vibration and shock well due to their sturdy design. Regular batteries are less resilient in harsh environments. This makes AGMs a better choice for rough terrains.
Mounting flexibility is another area where AGM batteries shine. Their sealed nature allows for installation in various orientations without leaking.
Cost is often a determining factor, with regular batteries being cheaper upfront. However, AGMs offer a longer lifespan and better reliability, which may offset initial expenses in the long run.
Environmentally, AGM batteries have an edge due to reduced acid spill risks. They also require less maintenance, contributing to less environmental pollution.
Here is a visual representation to summarize these differences:
Maintenance and Upkeep
Maintaining AGM batteries is straightforward. These batteries require little to no maintenance, making them quite user-friendly. This is particularly beneficial in environments where regular checks are not feasible.
Regular batteries, however, demand more attention. The electrolyte level needs monitoring and refilling. This routine maintenance can be cumbersome, especially for those unfamiliar with battery care.
AGM’s sealed design eliminates water evaporation issues. Users save time and effort, allowing for a more hassle-free experience. In contrast, regular batteries need regular checks to maintain optimal performance.
Regular batteries benefit from equalization charges to combat sulfation. This process can extend their life but adds to maintenance complexity.
Choosing between them often depends on your willingness to perform upkeep. AGM batteries appeal to users preferring minimal maintenance.
Vibration and Shock Resistance
AGM batteries offer superior resistance to vibration and shock. Their design helps them absorb impact, making them ideal for mobile applications.
Regular batteries, with their open design, struggle more with vibration. They are more prone to damage under harsh conditions.
This resistance to shock makes AGM batteries preferred in power sports and off-road applications. Durability in tough environments is essential, ensuring continuous performance.
Regular batteries require stable platforms to avoid vibrations. This limitation can be a barrier in certain use cases, such as marine or recreational vehicles.
AGM’s robust construction reduces downtime due to lessened physical wear. For those in rugged conditions, AGMs deliver long-term reliability.
Mounting Flexibility and Safety
AGM batteries boast excellent mounting versatility. Their sealed design means they can be installed in almost any orientation. This allows for creative placement and space-saving solutions.
Regular batteries, conversely, need to remain upright. Tilting them can lead to spills and corrosion. This limitation restricts their installation options, requiring more secure housing.
Safety considerations also favor AGMs. The absence of liquid spills reduces risk in sensitive applications.
For DIY projects, AGM batteries offer the convenience of not worrying about spills. This flexibility is appealing in cramped or awkward spaces.
Overall, AGM’s design ensures safer, easier handling. Users benefit from more installation options without sacrificing safety.
Charging Efficiency and Self-Discharge
AGM batteries excel in charging efficiency. They accept charge faster and more effectively than regular batteries. This advantage translates to less downtime, especially critical for frequent-use applications.
Their low self-discharge rate makes them ideal for long-term storage or infrequent use. AGMs retain power longer, ensuring readiness when needed.
Regular batteries, while more accommodating of different charging methods, require longer charging times. They risk higher self-discharge, leading to energy losses over time.
AGMs also maintain better charge retention during idle periods. This feature is beneficial for emergency backup systems or seasonal equipment.
The quick and efficient charging of AGMs makes them preferred in time-sensitive scenarios. Regular batteries, though cost-effective, may struggle in this regard.
Deep Cycle Capabilities
Deep cycle capabilities distinguish AGM batteries. They endure repeated charge and discharge cycles efficiently. This endurance makes them suitable for applications requiring sustained power output.
Regular batteries typically excel in short bursts of high power but less in deep cycling. Their performance may degrade faster with frequent cycling.
AGMs shine in renewable energy setups, where cycling is routine. This includes solar systems or off-grid living arrangements.
Frequent deep discharges can damage regular batteries. They are best suited for less demanding cycling needs.
In applications requiring prolonged energy use, AGMs offer reliability and longevity. Their design supports extensive cycling without compromising lifespan.
Cost Considerations and Value
Upfront cost often drives battery choice. Regular batteries generally have a lower initial price. This appeals to budget-conscious buyers.
AGM batteries, though more expensive initially, offer long-term savings. Their durability and minimal maintenance can balance out initial expenses over time.
Evaluating the total cost of ownership is critical. AGMs may reduce replacement frequency and upkeep costs.
For large-scale energy storage, regular batteries might be more economical if regular maintenance is feasible.
Ultimately, the decision often rests on balancing upfront cost against longevity and maintenance commitment. AGMs provide lasting value, especially where reliability is key.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
AGM batteries have an environmental edge, thanks to their sealed, maintenance-free design. They pose a lower risk of acid spills, which is kinder to the environment.
Regular batteries, with their liquid electrolyte, have higher spill risks. Proper disposal and careful handling are crucial to mitigate environmental harm.
Recycling both battery types is important. Regular batteries are easier to disassemble, promoting recycling. AGMs, though slightly more complex, are recyclable too.
Handling and disposal considerations make AGMs appealing in environmentally sensitive areas. Their design minimizes contamination risks.
Opting for AGM batteries can align with efforts to reduce environmental impacts. Their safer design and less frequent replacement needs support sustainability goals.
AGM Advantages: Why Choose AGM Over Regular Batteries?
AGM batteries offer notable advantages over regular batteries, making them a superior choice for many users. Their maintenance-free design is particularly appealing.
These batteries require no water replenishment, saving both time and effort. Their resilience to vibration and shock ensures reliability in demanding conditions.
AGM batteries have a lower self-discharge rate, making them ideal for storage. They retain their charge well during long idle periods.
Their quick charging capability further enhances their utility, especially when downtime is minimal. This is crucial for applications needing consistent power.
AGM batteries also stand out for their safety features. Their sealed design minimizes spill risks, making them safer for indoor use.
Furthermore, they emit less harmful gases, reducing ventilation requirements. This enhances safety in confined spaces.
Environmentally, AGM batteries are less prone to leaks. They are an eco-friendlier choice.
Their combination of durability, safety, and low maintenance makes AGMs an attractive option across various uses.
Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
AGM batteries perform excellently in extreme conditions, particularly in cold weather. Their low internal resistance allows them to efficiently deliver power, even when temperatures drop.
Regular batteries may falter in such environments due to thicker electrolyte fluid. AGMs handle temperature fluctuations better.
Their sealed design aids resistance to extreme heat. This feature can help prevent overheating issues common in regular batteries.
AGM batteries also retain their charge better under harsh conditions. They maintain operational readiness without frequent charging interruptions.
In extreme scenarios, AGM batteries provide the reliability needed. Their design ensures optimal performance, regardless of external challenges.
Enhanced Safety and Reliability
Safety and reliability are key benefits of AGM batteries. Their sealed construction prevents acid spills, a common issue with regular batteries.
AGMs are less likely to emit hydrogen gas during charging. This reduces explosion risks and ensures user safety.
Their robust design withstands physical stress, reducing the likelihood of damage from impacts. This trait boosts reliability significantly.
AGM batteries are also less prone to issues like sulfation. This translates to consistent performance over a longer period.
In critical applications, AGM batteries provide the peace of mind users seek. Their dependable nature ensures that power supply remains uninterrupted and safe.
Longevity and Durability
AGM batteries exhibit impressive longevity and durability. This is primarily due to their resilient design and efficient operation.
They withstand more charge-discharge cycles compared to regular batteries. This endurance makes them suitable for high-demand applications.
The use of high-purity lead contributes to their durability. It ensures a longer lifespan by minimizing plate degradation.
AGM batteries also resist corrosion better. This further extends their service life, offering long-term value.
Overall, AGMs provide a reliable investment. Their long life and robust nature make them an attractive choice for those seeking lasting power solutions.
Applications: Where AGM and Regular Batteries Excel
AGM and regular batteries both have their niches. Understanding these can aid in selecting the right battery for specific needs.
AGM batteries excel in situations needing reliability and safety. Their sealed design suits environments where spill and leak prevention is crucial.
They are common in off-grid systems, where minimal maintenance is vital. Their deep cycle ability fits the demands of renewable energy storage.
Regular batteries, on the other hand, are favored for more traditional automotive uses. They handle frequent start-ups efficiently due to their design.
AGM batteries work well in power sports, offering robustness against rough use. Their durability makes them ideal for marine and recreational applications.
In emergency and backup systems, both types have a role. AGMs provide high power discharge quickly, crucial when emergencies strike.
Regular batteries might be more economical for large-scale energy storage, provided maintenance can be managed. This is because they’re generally cheaper upfront.
Both battery types find places in telecommunication systems, with AGMs preferable for volatile environments. Their lower gas emission proves advantageous here.
Ultimately, the ideal choice depends on specific requirements, such as environment, budget, and maintenance capacity.
Automotive and Start-Stop Systems
In the automotive world, AGM batteries are preferred for start-stop systems. They handle frequent cycling efficiently, delivering reliable performance.
These batteries are designed to support vehicles with high electrical loads. This includes modern cars laden with electronic accessories.
Meanwhile, regular batteries thrive in conventional vehicles. They are cost-effective, providing enough energy for simple start mechanisms.
AGM batteries also ensure smoother starts in colder conditions. Their low internal resistance aids quick power delivery, essential in frigid temperatures.
For cars with intense power demands, AGMs provide an edge. Their robust construction caters to frequent high-demand scenarios effectively.
Renewable Energy Storage and Off-Grid Living
AGM batteries are ideal for renewable energy storage. Their deep cycling capability aligns well with solar and wind power systems.
They are maintenance-free, making them perfect for off-grid living. With less need for attention, they offer reliability and peace of mind.
AGMs can be stored for long periods without losing charge. This characteristic is beneficial for seasonal use and energy storage needs.
Their ability to handle varying discharge rates secures their position in renewable settings. Energy delivery is consistent, even when inputs vary.
In environments lacking consistent grid access, AGMs prove invaluable. They supply dependable power, critical for self-sustaining lifestyles.
Marine and Recreational Vehicles
Marine applications see significant benefits with AGM batteries. Their spill-proof nature suits the volatile aquatic environment perfectly.
In recreational vehicles, AGMs are preferred for their durability. They withstand vibration and rough handling typically encountered in these settings.
AGM batteries’ resilience to shock is crucial for off-road adventures. Consistent power delivery enhances trip reliability and safety.
For boats, their resistance to corrosion offers long service life. They require less upkeep, allowing more focus on leisure activities.
Regular batteries in such environments fall short. They require frequent maintenance, making AGMs the more convenient and reliable option.
Backup Power and Emergency Systems
In backup power systems, AGM batteries play an essential role. Their quick discharge and recharge abilities ensure readiness in emergencies.
Regular batteries might suit some backup scenarios. However, AGMs offer greater reliability where split-second energy availability is crucial.
AGM batteries’ longer life span justifies their use in high-stakes situations. Consistent power delivery is vital when human safety is involved.
Their lower self-discharge rate ensures they remain charged until needed. This is a key attribute for systems on standby for extended periods.
In conclusion, for emergency applications requiring prompt power and safety, AGM batteries stand out. They provide peace of mind with their reliable performance.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
Choosing between AGM and regular batteries depends on specific requirements and conditions. Consider factors like budget, maintenance capacity, and performance demands.
AGM batteries offer distinct advantages in environments needing reliability and minimal maintenance. Their sealed design and deep cycling capabilities excel in demanding situations.
Regular batteries may suit conventional applications, providing a more economical option if regular maintenance is feasible. Their upfront cost is generally lower.
Ultimately, aligning the battery choice with application needs and personal priorities will lead to optimal performance and satisfaction. Balancing cost, maintenance, and operational requirements will guide you to the right decision.




Leave a Reply